Here’s the crazy part: Your APN settings have a hidden gem called the Port field that most people completely ignore.
And guess what? It could be the secret to unlocking better mobile internet or fixing stubborn MMS issues.
In this guide, I’ll break down:
- What the Port field actually does.
- Why most networks leave it blank.
- And how setting it up correctly can change the way your phone connects to the internet.
If you’ve ever struggled with mobile data or MMS, this might be the answer you’ve been looking for. Let’s dive in and uncover the truth behind the Port field
The Port field in APN settings defines the gateway port used by mobile networks for services like MMS and WAP. Most modern networks leave it blank, but some require values like ‘8080’ or ‘9201’ for proper routing.
Quick Summary
- The Port field in APN settings defines the port number used for internet data transmission.
- It is often used alongside the Proxy setting to route network traffic.
- Most modern networks do not require a Port value; it is usually left blank.
- Some older networks, WAP services, and private enterprise APNs may still use specific Port settings.
- Incorrect Port values can cause internet connectivity issues, MMS failures, or slow browsing speeds.
- You can check and modify the Port field in APN settings on both Android and iOS devices.
- Resetting APN settings can resolve issues related to incorrect Port configurations.
What is the Port Field in APN Settings?
The Port field in APN settings is used to specify a network port number that directs data through a designated channel. It works in combination with the Proxy setting to manage internet traffic efficiently.
Primary Function
- Defines which port number should be used for data transmission.
- Helps route traffic through carrier-specified proxy servers.
- Required for WAP, MMS, or corporate VPNs in some cases.
- Used in older mobile networks but often left blank in modern setups.
Common Misconceptions
- “Changing the Port field improves internet speed.” → False. Port settings do not affect speed.
- “Every APN needs a Port value.” → False. Most networks do not require it.
- “Leaving the Port field blank will disable internet.” → False. Standard APNs work without a set Port.
How Does the Port Setting Affect Mobile Internet?
When is the Port Setting Needed?
- When using a Proxy server: Some mobile carriers require a specific port value for routing traffic.
- For WAP-based services: Older WAP (Wireless Application Protocol) configurations require a defined Port value.
- For MMS (Multimedia Messaging Services): Some carriers assign a specific Port for MMS routing.
- For private APNs and enterprise networks: Business networks with secure APNs may define a Port for access control.
When is the Port Setting Ignored?
- For most LTE and 5G connections: Modern mobile networks do not require a Port setting.
- When Proxy settings are not used: If the Proxy field is empty, the Port field is irrelevant.
- For general mobile internet browsing: Port settings do not affect standard data usage.
Do You Need to Configure the Port Field?
For most users, there is no need to configure the Port field manually. It is usually left blank because modern carriers handle network traffic dynamically.
Carrier-Specific Recommendations
| Carrier | Port Setting Requirement |
| AT&T | Not required (leave blank) |
| T-Mobile | Not required (leave blank) |
| Vodafone | Not required (leave blank) |
| Verizon | Not required (leave blank) |
| Enterprise Networks | May require specific Port numbers |
If your carrier provides a Port value, it should be entered exactly as instructed.
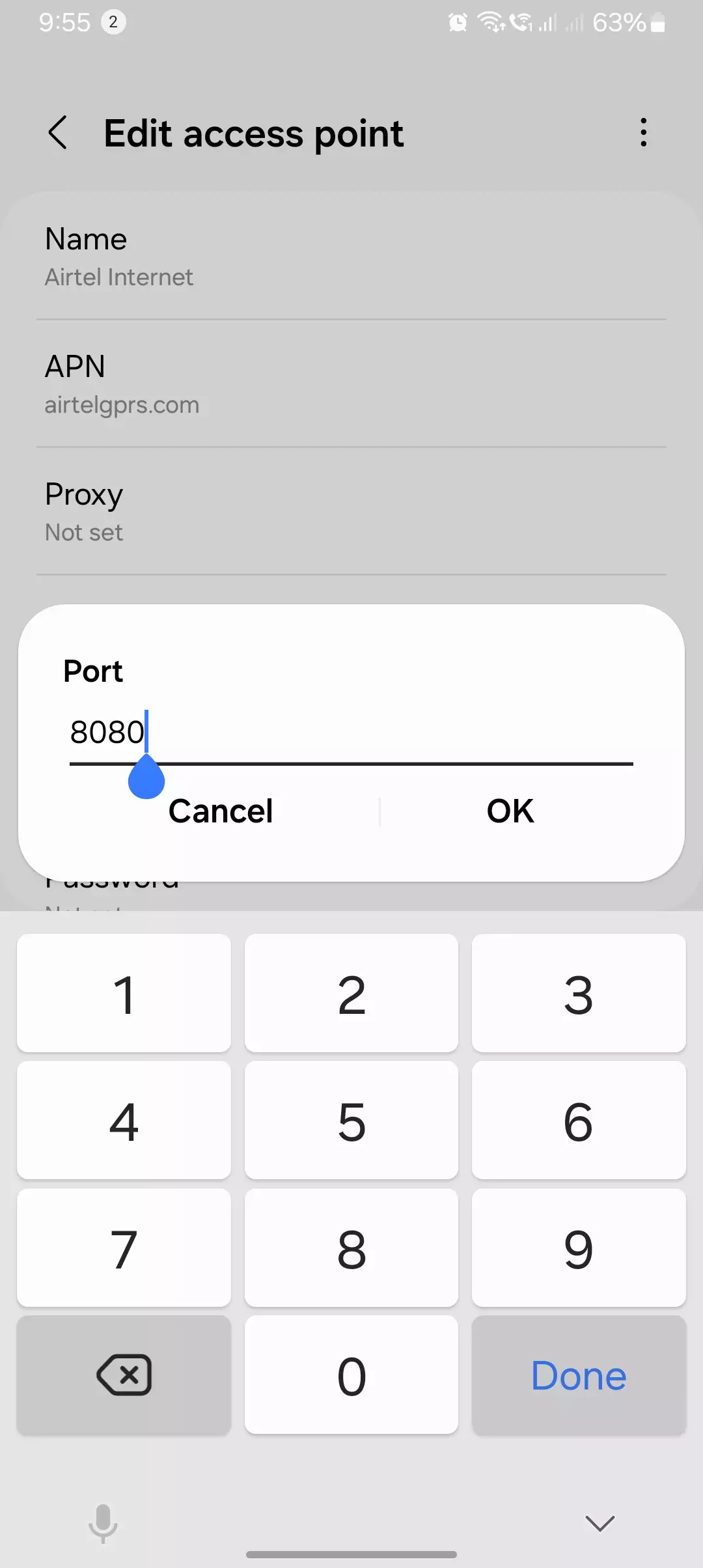
How to Check and Modify the Port Field in APN Settings
On Android
- Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Mobile Network.
- Select Advanced > Access Point Names (APN).
- Choose your carrier’s APN.
- Locate the Port field.
- Modify it if required and save changes.
On iOS (iPhone & iPad)
- Go to Settings > Cellular > Cellular Data Network.
- Scroll down to APN Settings.
- Find the Port field.
- Leave it blank unless instructed otherwise.
Troubleshooting: Port Setting Issues in APN
Symptoms of Incorrect Port Values
- No internet connection.
- Slow MMS sending or receiving.
- Network connection errors.
How to Fix APN Port Issues
- Reset APN settings to default (Settings > Reset Network Settings).
- Check carrier documentation for correct Port values.
- Restart your device after modifying APN settings.
- Contact carrier support if issues persist.
Port Setting and Network Security: VPNs, Proxies, and Private Networks
The Port field does not function like a VPN or Proxy but can be relevant in secure network configurations:
- VPN services bypass APN settings, including the Port field.
- Private networks may require custom APN Port assignments.
- Carriers sometimes block certain Ports for security reasons.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What happens if I leave the Port field blank?
Nothing. Most networks do not require a Port value.
Can I enter a random Port number?
No. Only enter a Port value if provided by your carrier.
Does changing the Port setting affect my internet speed?
No. Port settings do not impact speed or performance.
How do I find the correct Port value for my carrier?
Check your carrier’s official APN settings documentation.
Understanding APN Settings
APN settings serve as a bridge between your mobile device and your carrier’s data network. They ensure that your phone can send and receive data, multimedia messages (MMS), and use internet services correctly. Learn More about What is APN Settings in devices, here.
Main Components of an APN
| APN Component | Function |
| APN Name | Identifies the network assigned by the carrier |
| MCC & MNC | Mobile Country Code & Mobile Network Code, used for network identification |
| Proxy & Port | Proxy server address and port number for routing traffic |
| Server | Custom gateway address (rarely used) |
| MMSC | Multimedia Messaging Service Center URL |
| Authentication Type | Security method (PAP, CHAP, or none) |
| APN Type | Defines the purpose (e.g., default, MMS, SUPL, etc.) |
Among these, the Port field is specifically designed to work with the Proxy setting to define how network traffic is handled.
Conclusion
The Port field in APN settings is usually not required for modern mobile networks. It is only necessary for specific carrier settings, MMS, WAP, or private APNs. Leaving it blank is the best option unless instructed otherwise. If you experience issues, resetting your APN settings is often the simplest solution.
For accurate information, always refer to your carrier’s official APN settings before making changes.