Have you ever scrolled through your APN settings and stumbled upon the Server field thinking, ‘What even is this for?’ You’re not alone.
Most carriers leave this field blank, and it’s easy to ignore it… but what if I told you that understanding the Server field could be the key to fixing those annoying mobile internet issues?
In today’s breakdown, I’ll explain everything you need to know about the Server field in APN settings:
- What it is.
- Why it matters.
- And how you can configure it to make your connection smoother than ever.
Stick around because this one detail might just solve your internet problems once and for all.
Quick Summary
- The Server field in APN settings is mostly unused by modern carriers.
- It is a gateway field used for private networks, enterprise APNs, or specialized carrier settings.
- Most users do not need to configure this setting, as carriers typically leave it blank.
- It differs from the Proxy and MMSC fields, which have distinct roles in mobile data and MMS services.
- Modifying the Server field incorrectly usually does not affect internet connectivity but can be relevant in specific cases.
- You can check and edit APN settings in your Android or iOS device’s network settings menu.
- Resetting APN settings can fix server-related configuration errors if connectivity issues arise.
What is the Server Field in APN Settings?
The Server field in APN settings is designed to specify a custom server address that a mobile network might require for handling specific services. However, in most modern APN configurations, this field is left blank because it is not required for standard mobile data or MMS functionality.
Primary Function
- Acts as a gateway for special carrier services.
- May be required for corporate networks, VPN-based APNs, or legacy mobile data systems.
- Can be configured manually in rare cases where a carrier or enterprise network mandates it.

Common Misconceptions
- “If it’s blank, my internet won’t work.” → False. The Server field does not impact general internet access.
- “It works like a proxy.” → False. The Server field is different from Proxy settings, which manage traffic routing.
- “Entering any random server address will boost speed.” → False. Only carrier-specified values should be used.
How Does Server Setting Affect Mobile Internet?
The Server field in APN settings has little to no effect on most mobile internet connections, but it does play a role in certain scenarios:
When is the Server Field Needed?
- Custom APNs for businesses that need controlled network access.
- Legacy networks (2G/3G setups) that rely on specific gateway servers.
- Some MVNOs (Mobile Virtual Network Operators) may provide a server address for enhanced services.
- Private network APNs that use custom routing.
When is the Server Field Ignored?
- Most modern LTE and 5G networks do not require it.
- Standard carrier-provided APNs usually leave it blank.
- Changing it does not improve network speed or performance.
Understanding APN Settings
APN settings define how a mobile device connects to the internet through a carrier’s network. These settings include:
| APN Component | Function |
| APN Name | The network identifier assigned by the carrier |
| MCC & MNC | Mobile Country Code and Mobile Network Code, used for network identification |
| Proxy & Port | Defines an intermediary for network requests (rarely used) |
| Server | A custom gateway address for private networks (often left blank) |
| MMSC | URL for Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS) configuration |
| Authentication Type | Determines security protocols (PAP, CHAP, or none) |
| APN Type | Defines the purpose (e.g., default, MMS, SUPL, DUN, etc.) |
The Server field is not critical for standard mobile internet access but is present in APN settings for compatibility with custom setups. It acts as an intermediary gateway for specific network services, mainly for enterprise or private network configurations.
Do You Need to Configure the Server Field?
In 99% of cases, you do not need to enter anything in the Server field. Carriers usually leave this field empty because it does not impact data connectivity.
Carrier-Specific Recommendations
| Carrier | Server Setting Requirement |
| Vodafone | Not required (leave blank) |
| AT&T | Not required (leave blank) |
| Verizon | Not required (leave blank) |
| T-Mobile | Not required (leave blank) |
| Enterprise Networks | May require a custom server address |
If a carrier or employer provides a server address, it should be entered exactly as given.
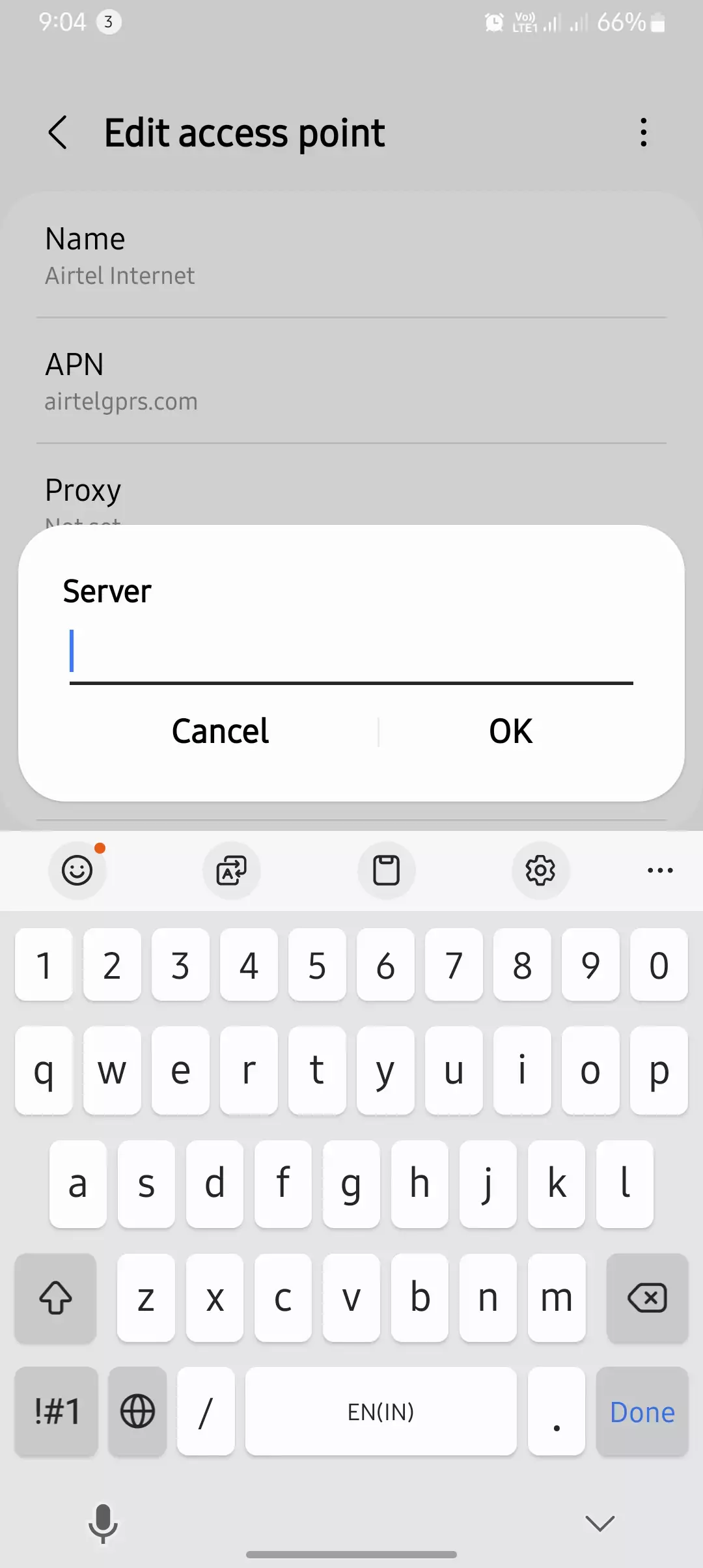
How to Check and Modify the Server Field in APN Settings
On Android
- Open Settings.
- Go to Network & Internet > Mobile Network.
- Tap Advanced > Access Point Names (APN).
- Select your carrier’s APN.
- Locate the Server field and check if it’s blank.
- Modify it if necessary and save changes.
On iOS (iPhone & iPad)
- Go to Settings > Cellular > Cellular Data Network.
- Scroll down to APN Settings.
- Find the Server field.
- Leave it blank unless instructed otherwise.
Troubleshooting: Server Setting Issues in APN
Symptoms of Incorrect Server Values
- No mobile data connection.
- Slow or inconsistent internet performance.
- Issues with MMS or VoLTE services.
How to Fix APN Server Issues
- Reset APN Settings to default values (Settings > Reset Network Settings).
- Check Carrier Documentation for any required server values.
- Reboot your device after modifying APN settings.
- Contact customer support if problems persist.
Server Field and VPNs, Proxies, and Private Networks
The Server field does not function like a VPN or Proxy but can be related in some cases:
- VPN services bypass APN settings, including the Server field.
- Enterprise networks may assign a custom APN Server address.
- Proxies work separately from the Server field, handling web traffic rather than core network routing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Does every APN need a Server field?
No. Most carriers leave it blank, and it’s not necessary for internet access.
Why is my Server field blank?
Because modern networks do not require it. Only specialized APNs use it.
Can I enter a random server address?
No. It must be provided by your carrier or network administrator.
Does changing the Server field affect my internet speed?
No. It does not impact speed or performance unless used for private routing.
Conclusion
The Server field in APN settings is generally unused for most mobile users. It is only relevant for specialized network configurations, and leaving it blank is the best approach unless instructed otherwise. If you experience issues, resetting your APN settings is often the simplest fix.
For accurate information, always check your carrier’s official APN settings before making changes.
1 thought on “What is Server in APN Settings? Everything You Need to Know”